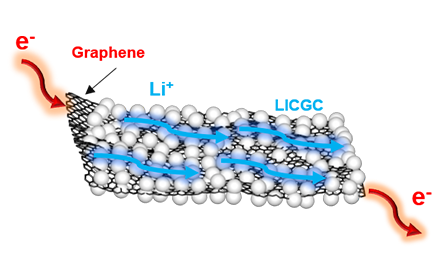
We demonstrate a facial and cost- effective synthesis approach of lithium-ion conducting glass ceramic (LICGC)/reduced graphene oxide (rGO) composite, in which the LICGC particles anchor on the rGO sheets densely and homogenously, forming a sandwich-like structure. The unique feature offers ultrafast Li-ion and electron pathways through the LICGC network and rGO sheets, resulting in the enhancement of the rate and cycle performances for the electrodes.
The transfer of lithium ions and electrons to the deep bulk of the electrode is made possible by adding this composite to the active material layer. This technology is also expected to be applied to the solid-state batteries.
Experimental method
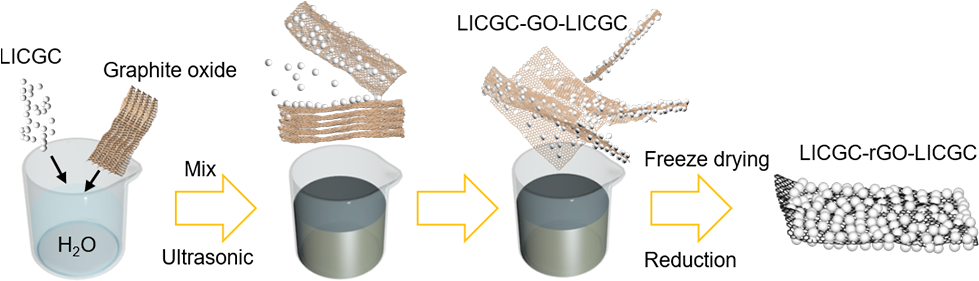
D. Ding, Y. Maeyoshi, M. Kubota, J. Wakasugi, K. Takemoto, Li-ion conducting glass ceramic ( LICGC )/ reduced graphene oxide sandwich-like structure composite for high-performance lithium-ion batteries, J. Power Sources. 500 (2021) 229976.
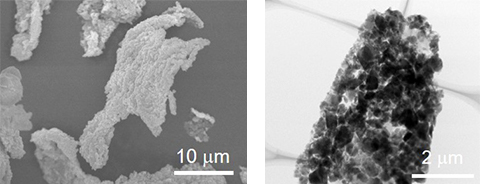
It was confirmed that LICGC was evenly placed on the graphene surface.
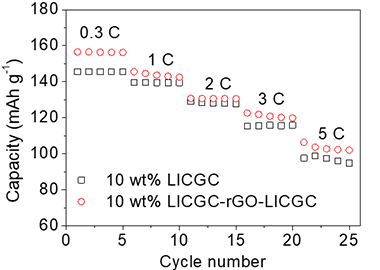
The rate performance was improved by adding LICGC/rGO than adding the LICGC only.
LICGC/rGO (marked as pink) were uniformly dispersed in the electrode to provide excellent electron and ionic conductive paths

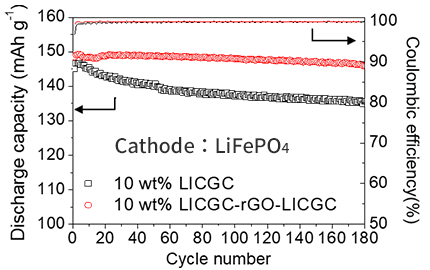
The discharge capacity after 180 cycles is 98.2% with LICGC/rGO and 93.4% without LICGC/rGO.
