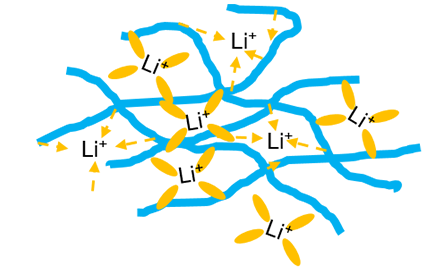
We report a super-concentrated polymer in “solvated ionic liquid” which is composed of polyethylene oxide (PEO), LiN(SO2CF3)2 (LiTFSI), and solvent with low viscosity (THF). It is found that the maximum coordination during Li, polymer, and the solvent can be formed by the molar ratio of PEO/Li = 1:1 with 25 wt% of solvent, left no free solvent exits in the mixture. The electrochemical performance of the designed electrolyte was evaluated by using a LiFePO4/Li cell. It has been further proven that incombustibility can be obtained by only adding ~15 wt% fire-retardant.
| Without SL | |
 |
 |
| 15 wt% SL | |
 |
 |
Flame retardancy was obtained by adding 15 wt% sulfolane (SL) as a fire-retardant to the solvated ionic liquid-polymer electrolyte.
D. Ding, Y. Maeyoshi, M. Kubota, J. Wakasugi, K. Kanamura, H. Abe, Non-flammable super-concentrated polymer electrolyte with “solvated ionic liquid” for lithium-ion batteries, J. Power Sources. 506 (2021) 230099.
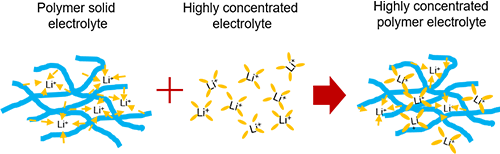
Polymer electrolyte in solvation ionic liquid can be seen as a combination of polymer electrolytes and concentrated electrolytes.
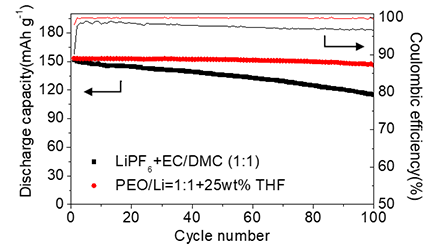
The discharge retention rate after 100 cycles is 95.5% for using the developed electrolyte (1:1 25 wt% THF) and 75.5% for the conventional organic electrolyte. Moreover, the developed electrolyte shows higher Coulomb efficiency.
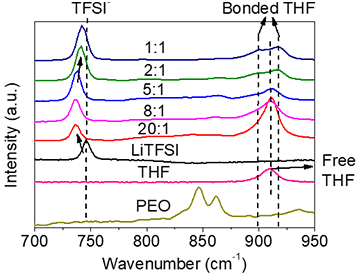
When the [EO] / Li <2: 1, THF content reaches 15 wt%, it can be estimated that the free THF molecule disappears and all PEO and THF are bound to Li+.
